
IRIS: Immersive Robot Interaction System
Immersive Robot Interaction System (IRIS) is a flexible framework designed to support immersive Human-Robot Interaction through Extended Reality (XR).
With IRIS, robot researchers no longer need to invest extensive effort in developing C# or Unity applications. Instead, IRIS streamlines the workflow and helps accelerate the research process.
The framework provides: - An open-source Python library called SimPublisher - The IRIS-Viz package - XR applications for multiple platforms
Using these components, researchers can directly use Python code in a seperate PC to display virtual objects in XR headsets and collect interaction data from XR devices.
System Architecture
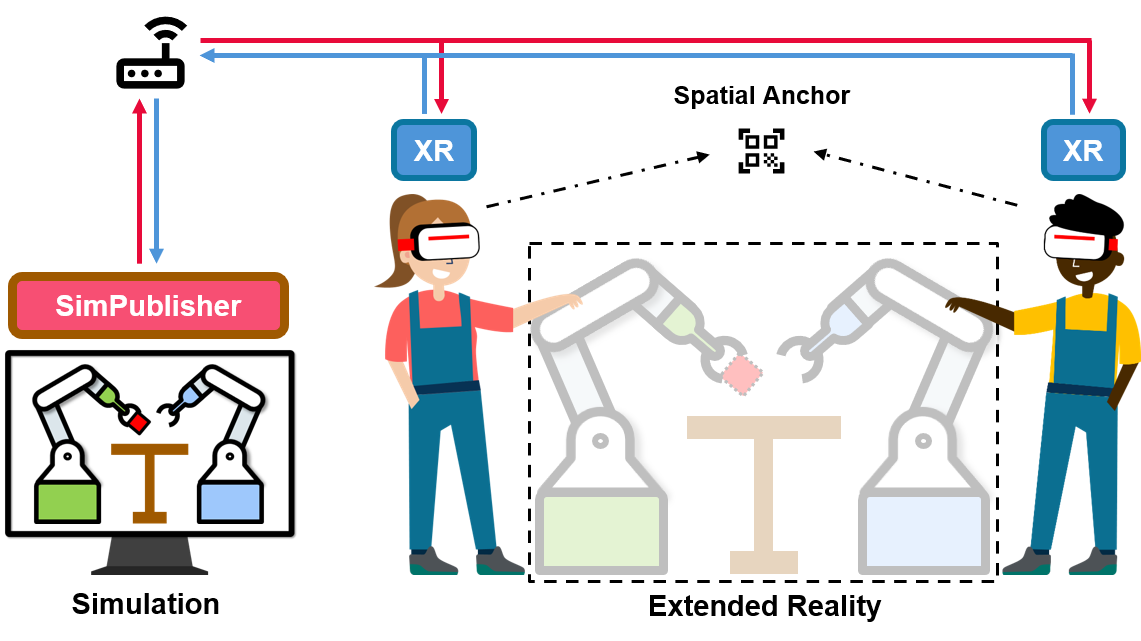
The IRIS system architecture supports interaction with robots in both simulation and the real world. All devices are connected through a Wi-Fi router.
Interact with Robots in Simulation
In the simulation paradigm, the scene is updated to all XR headsets through SimPublisher.
A spatial anchor aligns the virtual scenes across different headsets, ensuring consistent shared environments.
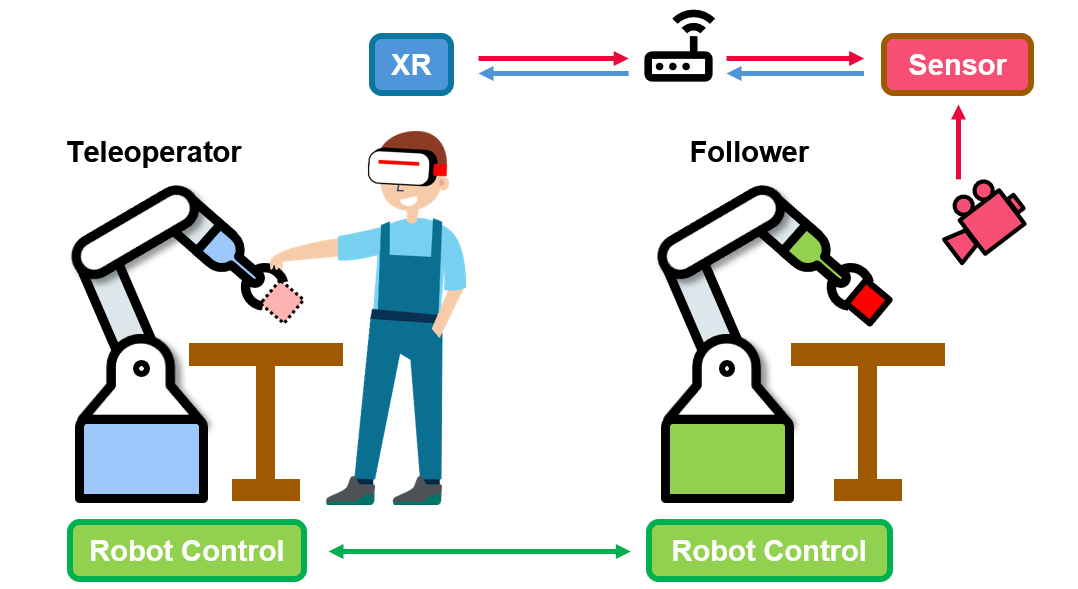
Interact with Robots in the Real World
In the real-world paradigm, a sensor generates a point cloud and transmits it to the XR headset.
This allows the teleoperator to clearly observe the manipulated object in front of the follower robot.
Features
IRIS is designed to generalize XR applications through five key features:
- Cross-Scene: unified representation of simulated objects for consistent scene rendering across simulators.
- Cross-Embodiment: compatibility with diverse robot configurations via modular modeling.
- Cross-Simulator: support for multiple simulators (e.g., MuJoCo, IsaacSim, CoppeliaSim, Genesis).
- Cross-Reality: integration across both simulated and real-world environments with data visualization tools.
- Cross-Platform: XR compatibility across different headsets, leveraging modular design for portability.
- Cross-User: multi-user collaboration and synchronized XR-based data collection.